Cerebral aneurysm and other vascular pathologies
Vascular pathologies of the brain are important pathologies among which the most known is the cerebral aneurysm.
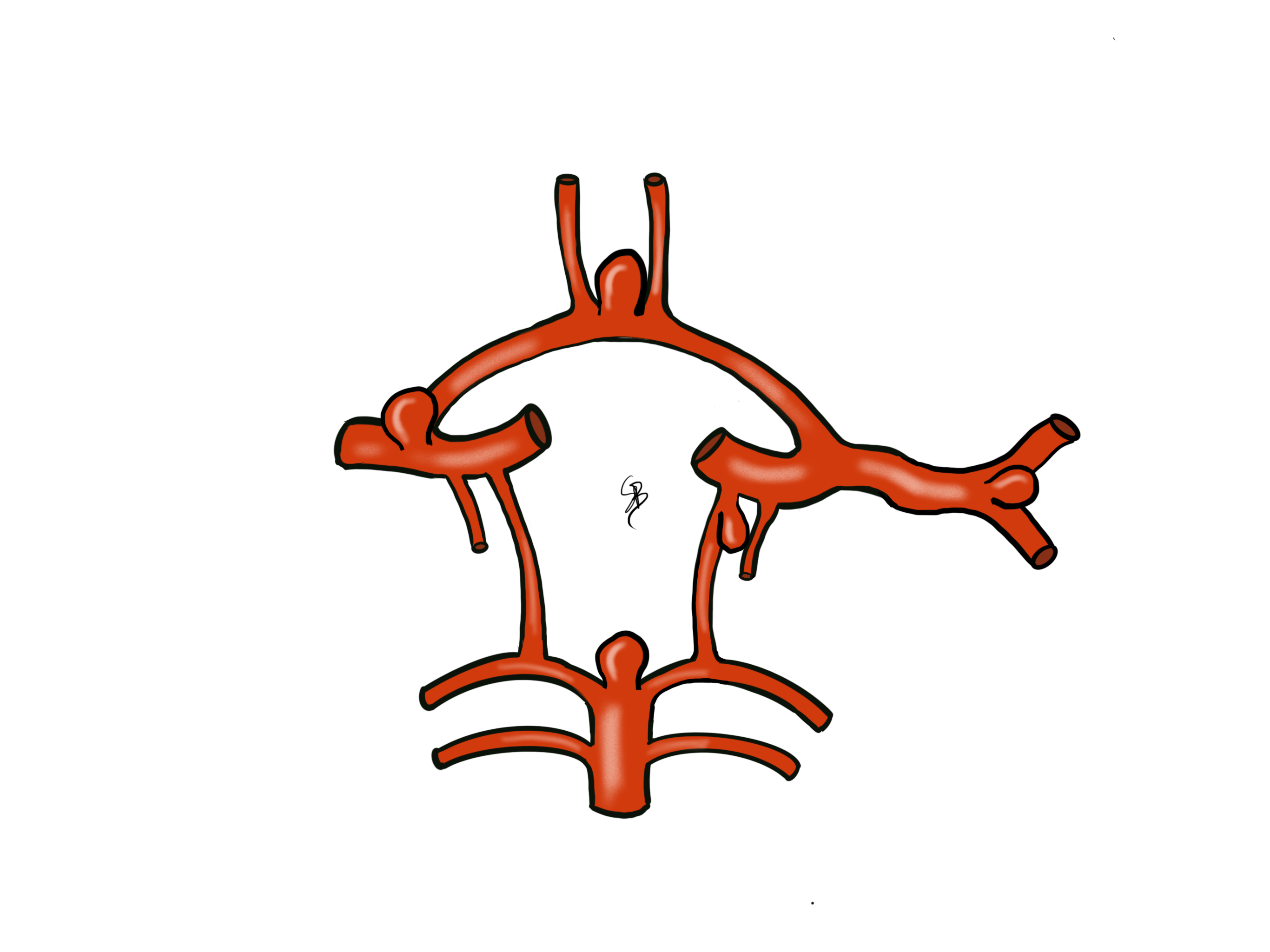
Multiple aneurysms on cerebral arteries
Cerebral aneurysm is due to the arterial wall degeneration. There is a slow process favoriting by common cardio-vascular risk factors (smoking, high blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes). Genetic factors also play a role in the formation of cerebral aneurysms. A cerebral aneurysm is rarely responsible for a neurologic deficit without bleeding. In rare cases of giant aneurysm, it could present a mass effect on cranial nerve for example.
It is frequent to occasionally discover a cerebral aneurysm, so a neurosurgical consultation is mandatory in such situation. Depending on case-by-case criteria, the risk for bleeding of the aneurysm is evaluated and consequently, the indication or not to treat such aneurysm. Risk factors that increased the risk of bleeding are the aneurysmal sac diameter > 7mm, the localization in posterior circulation, smoking, high blood pressure, familial history.
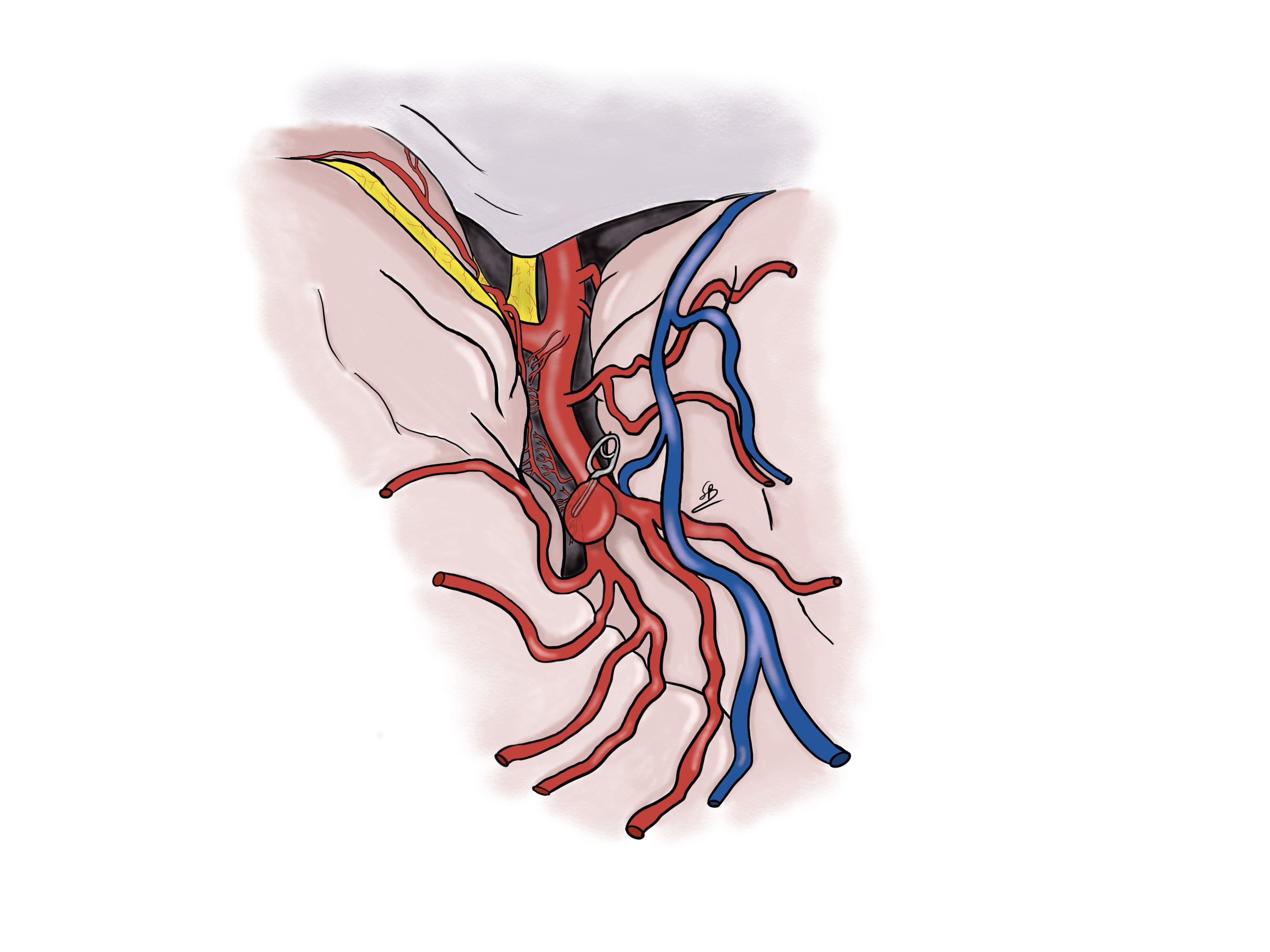
Aneurism clipping
Two different treatments to exclude the aneurysm from the arterial circulation are available: the microsurgical clipping and the endovascular coiling. Dr Robert and Dr Bonasia have an important experience in the aneurysmal clipping. They realized more than 200 surgeries for this pathology. This is a treatment they propose at Clinique La Source in Lausanne.
A cavernoma or cavernous angioma is a vascular pathology of the central nervous system which is defined as a venous mass in the cerebral parenchyma or in the medulla. Most frequent clinical signs are seizures, motor deficit and headache. The classical treatment is the microsurgical resection under general anesthesia. Alternative treatments as radiotherapy are limited to inaccessible lesions.
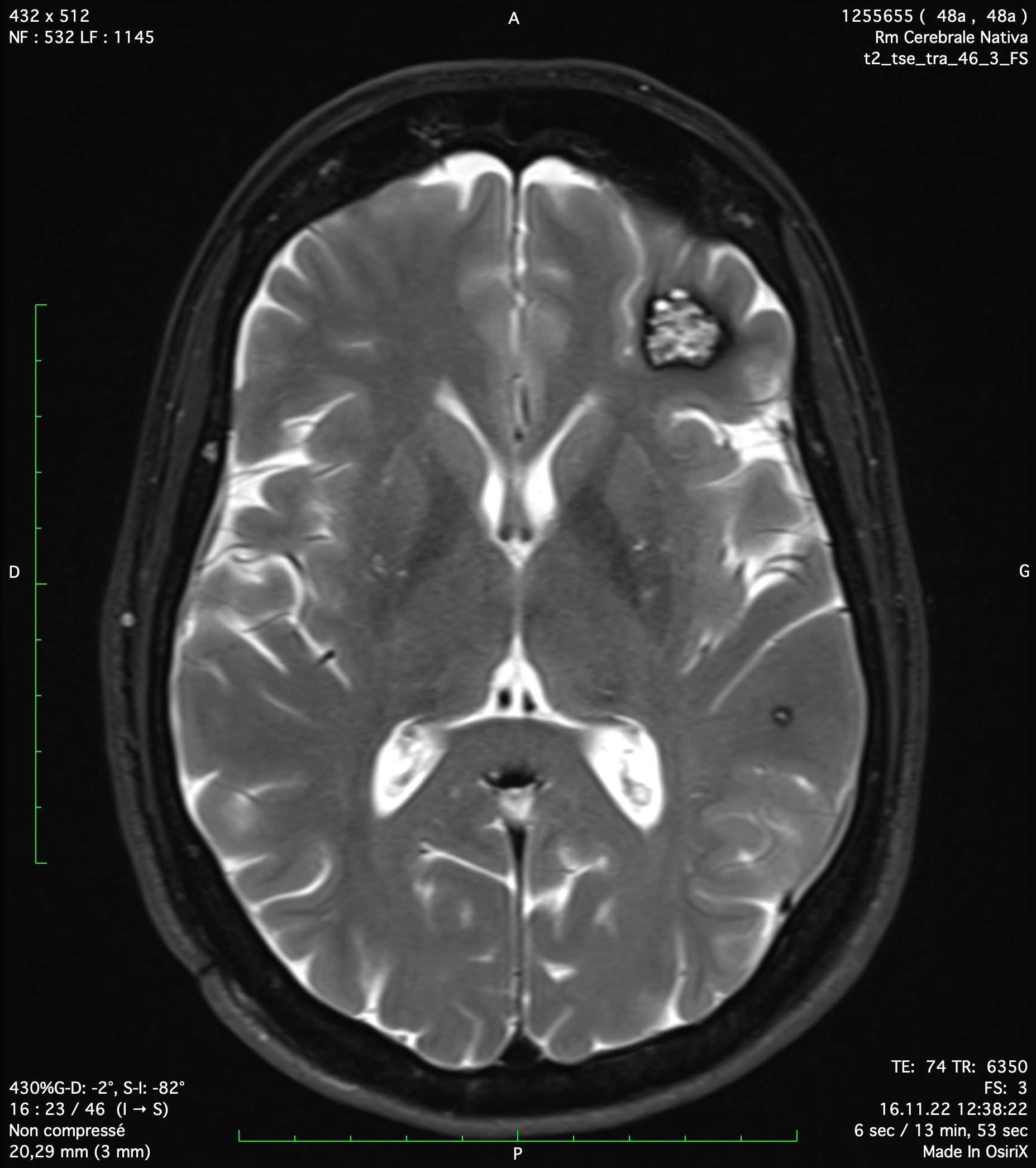
Cerebral cavernoma
Fortunately, most of cerebral cavernomas are asymptomatic and stable. In these cases, there is no indication for a treatment and only a radiological follow-up is necessary. Dr Robert and Dr Bonasia have an important experience in follow-up and surgical treatment of cerebral cavernomas. This is a treatment they propose at Clinique La Source in Lausanne.
Cerebral arterio-venous malformations (AVM) are complex neuro-vascular pathologies. An AVM is a malformation inside of the brain parenchyma that involve cerebral arteries and cerebral veins. Even if AVMs have not a tendency to increase in size, they could lead to important neurological deficit in case of bleeding. As other vascular pathologies, most of cerebral AVMs do not bleed and only a radiological follow-up is necessary. In case of indication for a treatment, the three different treatments are the microsurgical resection, the endovascular embolization and the radiosurgical irradiation. These three treatments could be combined to completely treat an AVM. Multi-disciplinary discussion is mandatory to adopt the right therapeutic strategy. Dr Robert and Dr Bonasia have an important experience in follow-up and surgical treatment of cerebral AVMs. This is a treatment they propose at Clinique La Source in Lausanne.
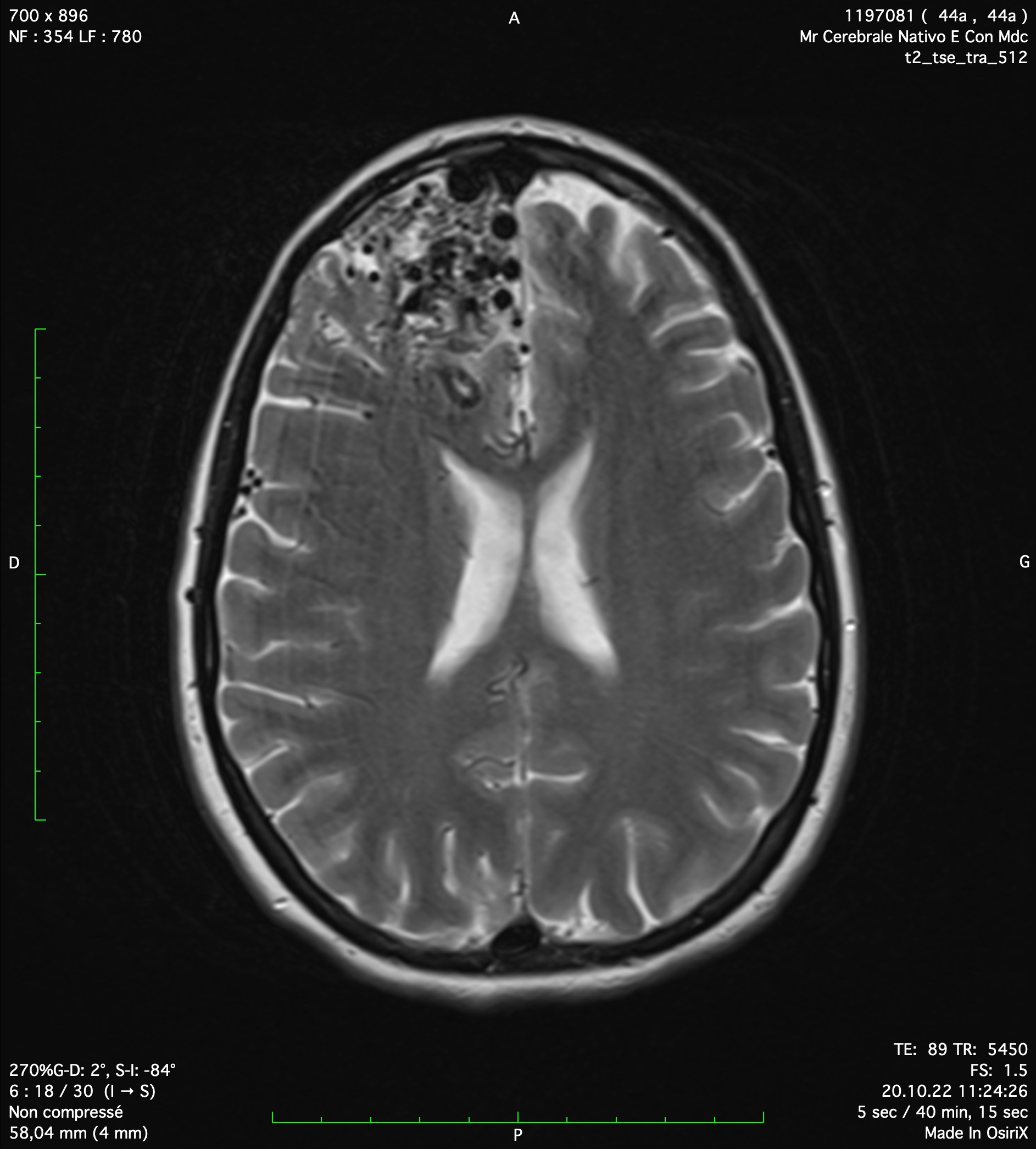
Arterio-venous malformation
